Quickstart: Ionic Vue
Intro
This example provides the steps to build a simple user management app (from scratch!) using Supabase and Ionic Vue. It includes:
- Supabase Database: a Postgres database for storing your user data.
- Supabase Auth: users can sign in with magic links (no passwords, only email).
- Supabase Storage: users can upload a photo.
- Row Level Security: data is protected so that individuals can only access their own data.
- Instant APIs: APIs will be automatically generated when you create your database tables.
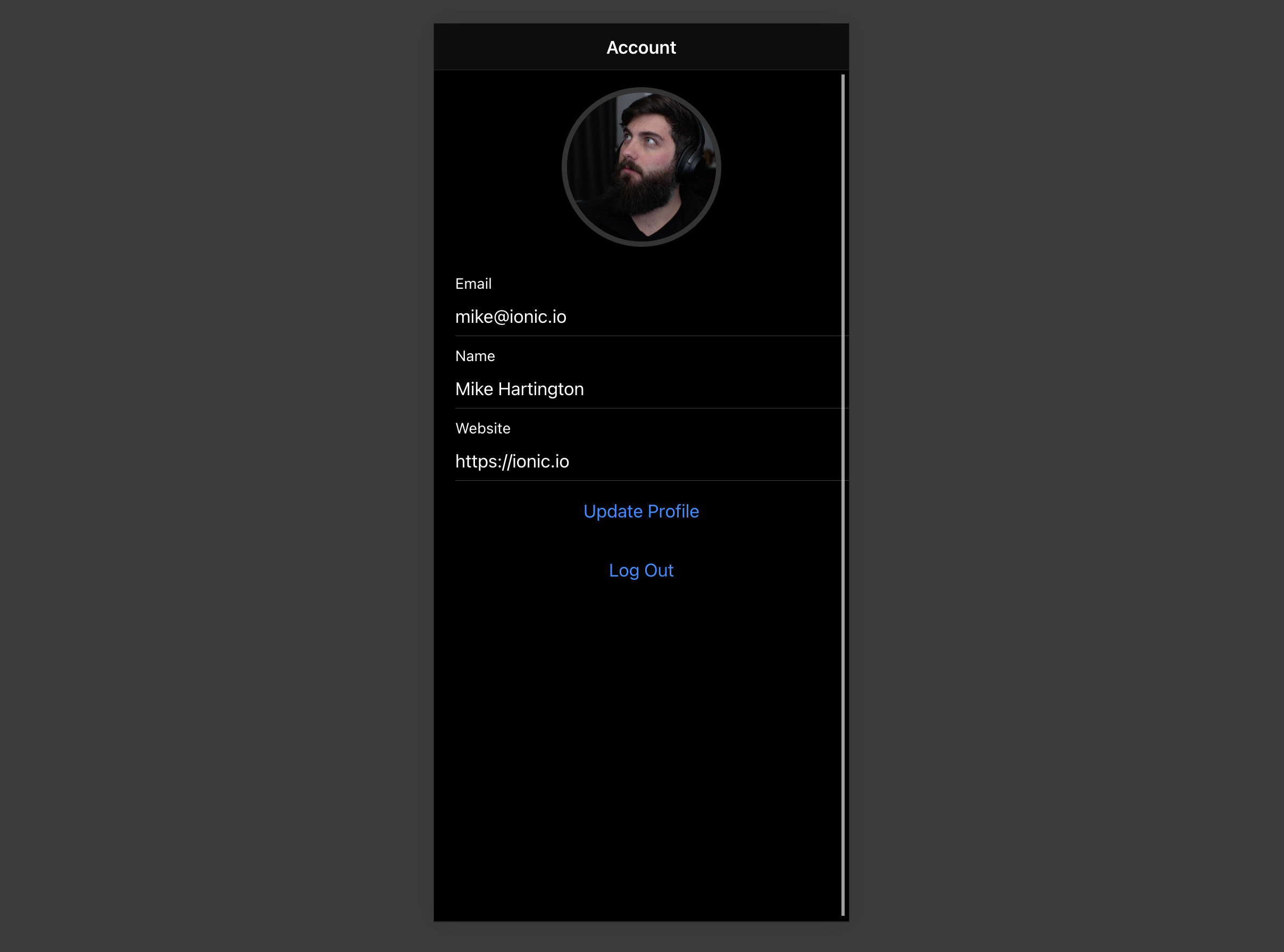
By the end of this guide you'll have an app which allows users to login and update some basic profile details:
Clicking this button the application will:
- Launch and prepare the Postgres database in Supabase.
- Launch the app in Vercel.
- Fork the example into your own GitHub account.
- Prepare the deployed application with all the necessary environment variables.
If you want to do it yourself, let's get started!
GitHub
Whenever you get stuck at any point, take a look at this repo.
Project set up
Before we start building we're going to set up our Database and API. This is as simple as starting a new Project in Supabase and then creating a "schema" inside the database.
Create a project
- Go to app.supabase.com.
- Click on "New Project".
- Enter your project details.
- Wait for the new database to launch.
Set up the database schema
Now we are going to set up the database schema. We can use the "User Management Starter" quickstart in the SQL Editor, or you can just copy/paste the SQL from below and run it yourself.
- Dashboard
- SQL
- Go to the SQL Editor page in the Dashboard.
- Click User Management Starter.
- Click Run.
-- Create a table for public "profiles"
create table profiles (
id uuid references auth.users not null,
updated_at timestamp with time zone,
username text unique,
avatar_url text,
website text,
primary key (id),
unique(username),
constraint username_length check (char_length(username) >= 3)
);
alter table profiles enable row level security;
create policy "Public profiles are viewable by everyone."
on profiles for select
using ( true );
create policy "Users can insert their own profile."
on profiles for insert
with check ( auth.uid() = id );
create policy "Users can update own profile."
on profiles for update
using ( auth.uid() = id );
-- Set up Realtime!
begin;
drop publication if exists supabase_realtime;
create publication supabase_realtime;
commit;
alter publication supabase_realtime add table profiles;
-- Set up Storage!
insert into storage.buckets (id, name)
values ('avatars', 'avatars');
create policy "Avatar images are publicly accessible."
on storage.objects for select
using ( bucket_id = 'avatars' );
create policy "Anyone can upload an avatar."
on storage.objects for insert
with check ( bucket_id = 'avatars' );
Get the API Keys
Now that you've created some database tables, you are ready to insert data using the auto-generated API.
We just need to get the URL and anon key from the API settings.
- Go to the Settings page in the Dashboard.
- Click API in the sidebar.
- Find your API
URL,anon, andservice_rolekeys on this page.
Building the App
Let's start building the Vue app from scratch.
Initialize an Ionic Vue app
We can use the Ionic CLI to initialize
an app called supabase-ionic-vue:
npm install -g @ionic/cli
ionic start supabase-ionic-vue blank --type vue
cd supabase-ionic-vue
Then let's install the only additional dependency: supabase-js
npm install @supabase/supabase-js
And finally we want to save the environment variables in a .env.
All we need are the API URL and the anon key that you copied earlier.
VUE_APP_SUPABASE_URL=YOUR_SUPABASE_URL
VUE_APP_SUPABASE_ANON_KEY=YOUR_SUPABASE_ANON_KEY
Now that we have the API credentials in place, let's create a helper file to initialize the Supabase client. These variables will be exposed on the browser, and that's completely fine since we have Row Level Security enabled on our Database.
import { createClient } from '@supabase/supabase-js';
const supabaseUrl = process.env.VUE_APP_SUPABASE_URL as string;
const supabaseAnonKey = process.env.VUE_APP_SUPABASE_ANON_KEY as string;
export const supabase = createClient(supabaseUrl, supabaseAnonKey);
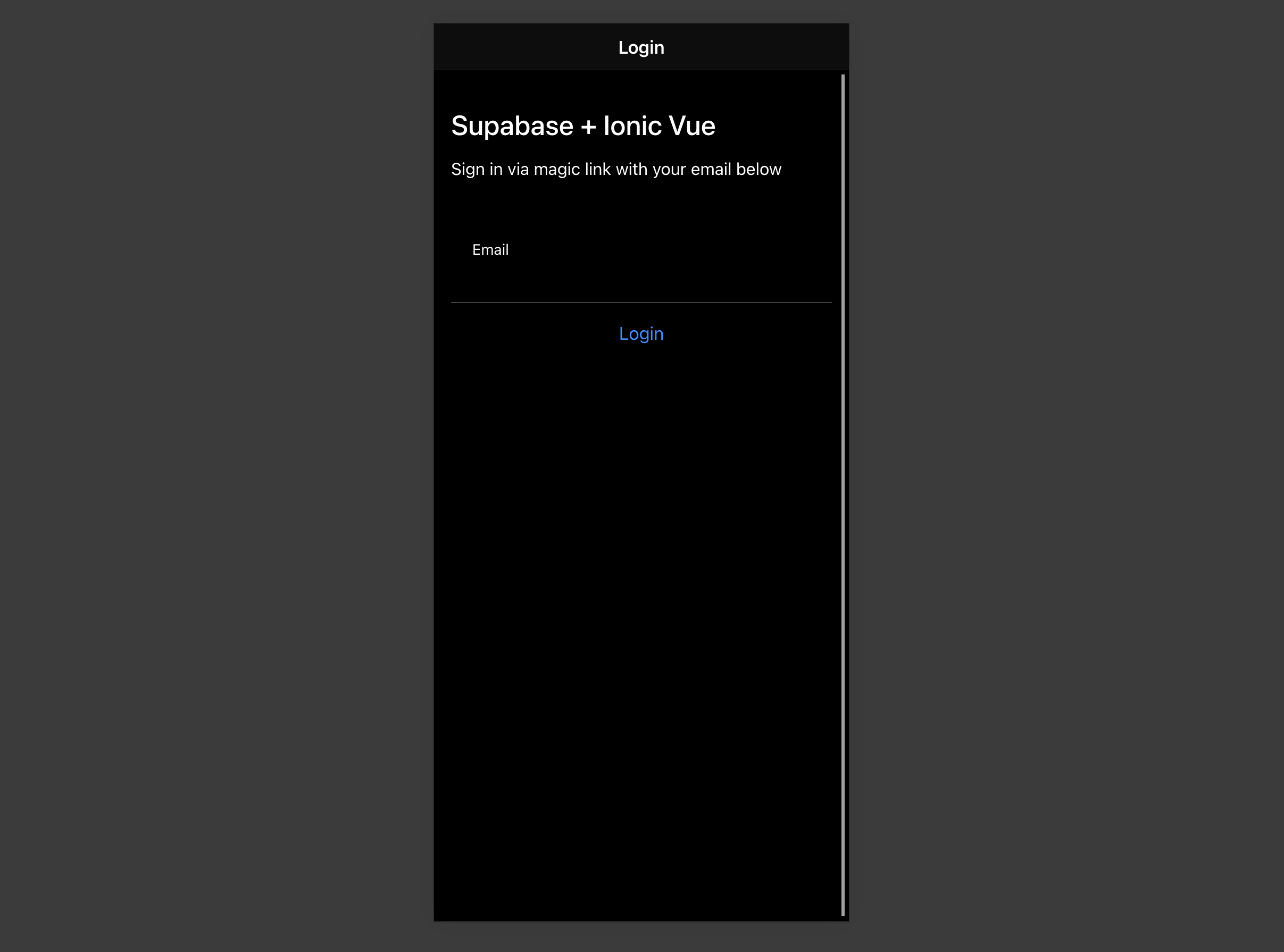
Set up a Login route
Let's set up a Vue component to manage logins and sign ups. We'll use Magic Links, so users can sign in with their email without using passwords.
<template>
<ion-page>
<ion-header>
<ion-toolbar>
<ion-title>Login</ion-title>
</ion-toolbar>
</ion-header>
<ion-content>
<div class="ion-padding">
<h1>Supabase + Ionic Vue</h1>
<p>Sign in via magic link with your email below</p>
</div>
<ion-list inset="true">
<form @submit.prevent="handleLogin">
<ion-item>
<ion-label position="stacked">Email</ion-label>
<ion-input
v-model="email"
name="email"
autocomplete
type="email"
></ion-input>
</ion-item>
<div class="ion-text-center">
<ion-button type="submit" fill="clear">Login</ion-button>
</div>
</form>
</ion-list>
<p>{{email}}</p>
</ion-content>
</ion-page>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { supabase } from '../supabase';
import {
IonContent,
IonHeader,
IonPage,
IonTitle,
IonToolbar,
IonList,
IonItem,
IonLabel,
IonInput,
IonButton,
toastController,
loadingController,
} from '@ionic/vue';
import { defineComponent, ref } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'LoginPage',
components: {
IonContent,
IonHeader,
IonPage,
IonTitle,
IonToolbar,
IonList,
IonItem,
IonLabel,
IonInput,
IonButton,
},
setup() {
const email = ref('');
const handleLogin = async () => {
const loader = await loadingController.create({});
const toast = await toastController.create({ duration: 5000 });
try {
await loader.present();
const { error } = await supabase.auth.signIn({ email: email.value });
if (error) throw error;
toast.message = 'Check your email for the login link!';
await toast.present();
} catch (error: any) {
toast.message = error.error_description || error.message;
await toast.present();
} finally {
await loader.dismiss();
}
};
return { handleLogin, email };
},
});
</script>
Account page
After a user is signed in we can allow them to edit their profile details and manage their account.
Let's create a new component for that called Account.vue.
<template>
<ion-page>
<ion-header>
<ion-toolbar>
<ion-title>Account</ion-title>
</ion-toolbar>
</ion-header>
<ion-content>
<form @submit.prevent="updateProfile">
<ion-item>
<ion-label>
<p>Email</p>
<p>{{ session?.user?.email }}</p>
</ion-label>
</ion-item>
<ion-item>
<ion-label position="stacked">Name</ion-label>
<ion-input
type="text"
name="username"
v-model="profile.username"
></ion-input>
</ion-item>
<ion-item>
<ion-label position="stacked">Website</ion-label>
<ion-input
type="url"
name="website"
v-model="profile.website"
></ion-input>
</ion-item>
<div class="ion-text-center">
<ion-button fill="clear" type="submit">Update Profile</ion-button>
</div>
</form>
<div class="ion-text-center">
<ion-button fill="clear" @click="signOut">Log Out</ion-button>
</div>
</ion-content>
</ion-page>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { store } from '@/store';
import { supabase } from '@/supabase';
import {
IonContent,
IonHeader,
IonPage,
IonTitle,
IonToolbar,
toastController,
loadingController,
IonInput,
IonItem,
IonButton,
IonLabel,
} from '@ionic/vue';
import { User } from '@supabase/supabase-js';
import { defineComponent, onMounted, ref } from 'vue';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'AccountPage',
components: {
IonContent,
IonHeader,
IonPage,
IonTitle,
IonToolbar,
IonInput,
IonItem,
IonButton,
IonLabel,
},
setup() {
const session = ref(supabase.auth.session());
const profile = ref({
username: '',
website: '',
avatar_url: '',
});
const user = store.user as User;
async function getProfile() {
const loader = await loadingController.create({});
const toast = await toastController.create({ duration: 5000 });
await loader.present();
try {
let { data, error, status } = await supabase
.from('profiles')
.select(`username, website, avatar_url`)
.eq('id', user.id)
.single();
if (error && status !== 406) throw error;
if (data) {
console.log(data)
profile.value = {
username: data.username,
website: data.website,
avatar_url: data.avatar_url,
};
}
} catch (error: any) {
toast.message = error.message;
await toast.present();
} finally {
await loader.dismiss();
}
}
const updateProfile = async () => {
const loader = await loadingController.create({});
const toast = await toastController.create({ duration: 5000 });
try {
await loader.present();
const updates = {
id: user.id,
...profile.value,
updated_at: new Date(),
};
//
let { error } = await supabase.from('profiles').upsert(updates, {
returning: 'minimal', // Don't return the value after inserting
});
//
if (error) throw error;
} catch (error: any) {
toast.message = error.message;
await toast.present();
} finally {
await loader.dismiss();
}
};
async function signOut() {
const loader = await loadingController.create({});
const toast = await toastController.create({ duration: 5000 });
await loader.present();
try {
let { error } = await supabase.auth.signOut();
if (error) throw error;
} catch (error: any) {
toast.message = error.message;
await toast.present();
} finally {
await loader.dismiss();
}
}
onMounted(() => {
getProfile();
});
return { signOut, profile, session, updateProfile };
},
});
</script>
Launch!
Now that we have all the components in place, let's update App.vue and our routes:
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from '@ionic/vue-router';
import { RouteRecordRaw } from 'vue-router';
import LoginPage from '../views/Login.vue';
import AccountPage from '../views/Account.vue';
const routes: Array<RouteRecordRaw> = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Login',
component: LoginPage
},
{
path: '/account',
name: 'Account',
component: AccountPage
}
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(process.env.BASE_URL),
routes
})
export default router
<template>
<ion-app>
<ion-router-outlet />
</ion-app>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { IonApp, IonRouterOutlet, useIonRouter } from '@ionic/vue';
import { defineComponent } from 'vue';
import { store } from './store';
import { supabase } from './supabase';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'App',
components: {
IonApp,
IonRouterOutlet
},
setup(){
const router = useIonRouter();
store.user = supabase.auth.user() ?? {};
supabase.auth.onAuthStateChange((_, session) => {
store.user = session?.user ?? {}
if(session?.user) {
router.replace('/account');
}
})
}
});
</script>
Once that's done, run this in a terminal window:
ionic serve
And then open the browser to localhost:3000 and you should see the completed app.
Bonus: Profile photos
Every Supabase project is configured with Storage for managing large files like photos and videos.
Create an upload widget
First install two packages in order to interact with the user's camera.
npm install @ionic/pwa-elements @capacitor/camera
CapacitorJS is a cross platform native runtime from Ionic that enables web apps to be deployed through the app store and provides access to native deavice API.
Ionic PWA elements is a companion package that will polyfill certain browser APIs that provide no user interface with custom Ionic UI.
With those packages installed we can update our main.ts to include an additional bootstapping call for the Ionic PWA Elements.
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router';
import { IonicVue } from '@ionic/vue';
/* Core CSS required for Ionic components to work properly */
import '@ionic/vue/css/ionic.bundle.css';
/* Theme variables */
import './theme/variables.css';
import { defineCustomElements } from '@ionic/pwa-elements/loader';
defineCustomElements(window);
const app = createApp(App)
.use(IonicVue)
.use(router);
router.isReady().then(() => {
app.mount('#app');
});
Then create an AvatarComponent.
<template>
<div class="avatar">
<div class="avatar_wrapper" @click="uploadAvatar">
<img v-if="avatarUrl" :src="avatarUrl" />
<ion-icon v-else name="person" class="no-avatar"></ion-icon>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { ref, toRefs, watch, defineComponent } from 'vue';
import { supabase } from '../supabase';
import { Camera, CameraResultType } from '@capacitor/camera';
import { IonIcon } from '@ionic/vue';
import { person } from 'ionicons/icons';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'AppAvatar',
props: { path: String },
emits: ['upload', 'update:path'],
components: { IonIcon },
setup(prop, { emit }) {
const { path } = toRefs(prop);
const avatarUrl = ref('');
const downloadImage = async () => {
try {
const { data, error } = await supabase.storage
.from('avatars')
.download(path.value);
if (error) throw error;
avatarUrl.value = URL.createObjectURL(data!);
} catch (error: any) {
console.error('Error downloading image: ', error.message);
}
};
const uploadAvatar = async () => {
try {
const photo = await Camera.getPhoto({
resultType: CameraResultType.DataUrl,
});
if (photo.dataUrl) {
const file = await fetch(photo.dataUrl)
.then((res) => res.blob())
.then(
(blob) =>
new File([blob], 'my-file', { type: `image/${photo.format}` })
);
const fileName = `${Math.random()}-${new Date().getTime()}.${
photo.format
}`;
let { error: uploadError } = await supabase.storage
.from('avatars')
.upload(fileName, file);
if (uploadError) {
throw uploadError;
}
emit('update:path', fileName);
emit('upload');
}
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
};
watch(path, () => {
if (path.value) downloadImage();
});
return { avatarUrl, uploadAvatar, person };
},
});
</script>
<style>
.avatar {
display: block;
margin: auto;
min-height: 150px;
}
.avatar .avatar_wrapper {
margin: 16px auto 16px;
border-radius: 50%;
overflow: hidden;
height: 150px;
aspect-ratio: 1;
background: var(--ion-color-step-50);
border: thick solid var(--ion-color-step-200);
}
.avatar .avatar_wrapper:hover {
cursor: pointer;
}
.avatar .avatar_wrapper ion-icon.no-avatar {
width: 100%;
height: 115%;
}
.avatar img {
display: block;
object-fit: cover;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
Add the new widget
And then we can add the widget to the Account page:
<template>
<ion-page>
<ion-header>
<ion-toolbar>
<ion-title>Account</ion-title>
</ion-toolbar>
</ion-header>
<ion-content>
<avatar v-model:path="profile.avatar_url" @upload="updateProfile"></avatar>
...
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import Avatar from '../components/Avatar.vue';
export default defineComponent({
name: 'AccountPage',
components: {
Avatar,
....
}
</script>
Next steps
At this stage you have a fully functional application!
- Got a question? Ask here.
- Sign in: app.supabase.com