Database Connections
Supabase provides several options for programmatically connecting to your Postgres database:
Types of Connection
- HTTP connections using the API.
- Direct connections using Postgres' standard connection system.
- Connection pooling using PgBouncer.
API vs Direct vs Pooling
- The API is an auto-generated REST interface. You should use this for all browser and application interactions.
- A "direct connection" is when a connection is made to the database using Postgres' native connection implementation. You should use this for tools which are always alive - usually installed on a long-running server.
- A "connection pool" is a system (external to Postgres) which keeps connections "open". You should use this for serverless functions and tools which disconnect from the database frequently.
Why would you use a connection pool? Primarily because the way that Postgres handles connections isn't very scalable for a large number of temporary connections. You can use these simple questions to determine which connection method to use:
- Are you connecting to a database and maintaining a connection? If yes, use a direct connection.
- Are you connecting to your database and then disconnecting immediately (e.g. a serverless environment)? If yes, use a connection pool.
API
Supabase provides an auto-updating API. This is the easiest way to get started if you are managing data (fetching, inserting, updating).
Interfaces
We provides several types of API to suit your preferences and use-case:
- REST: interact with your database through a REST interface.
- GraphQL: interact with your database through a GraphQL interface.
- Realtime: listen to database changes over websockets.
You cannot manage the database schema via the API (for security reasons). To do that you can use the dashboard or connect directly to your database.
API URL and Keys
You can find the API URL and Keys in the Dashboard.
Direct connections
Every Supabase project provides a full Postgres database. You can connect to the database using any tool which supports Postgres.
Finding your connection string
- Go to the
Settingssection. - Click
Database. - Find your Connection Info and Connection String. Direct connections are on port
5432.
Connection Pool
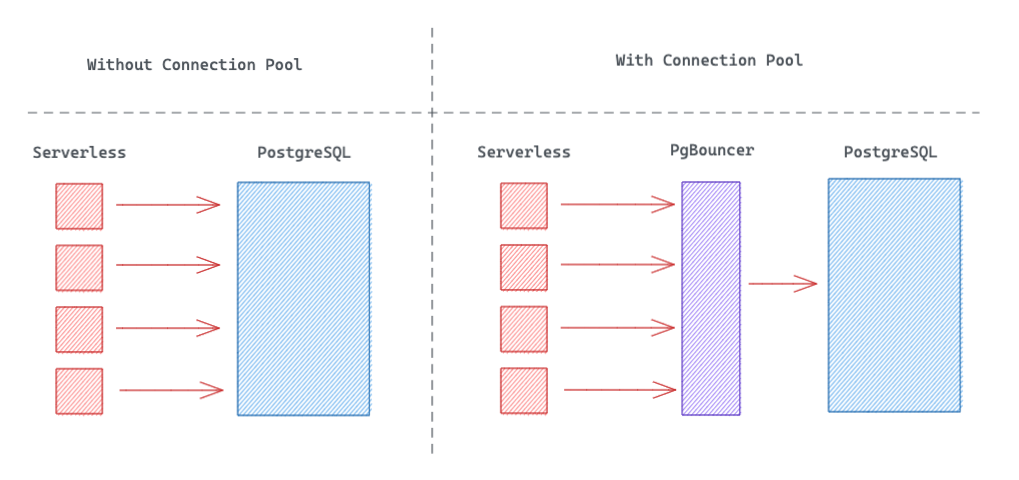
Connection pools are useful for managing a large number of temporary connections. For example, if you are using Prisma deployed to a Serverless environment.
How connection pooling works
A "connection pool" is a system (external to Postgres) which manages connections, rather than PostgreSQL's native system. Supabase uses PgBouncer for connection pooling.
When a client makes a request, PgBouncer "allocates" an available connection to the client. When the client transaction or session is completed the connection is returned to the pool and is free to be used by another client.
Pool modes
Pool Mode determines how PgBouncer handles a connection.
Session
When a new client connects, a connection is assigned to the client until it disconnects. Afterward, the connection is returned back to the pool.
All PostgreSQL features can be used with this option.
Transaction
This is the suggested option for serverless functions. A connection is only assigned to the client for the duration of a transaction. Two consecutive transactions from the same client could be executed over two different connections.
Some session-based PostgreSQL features such as prepared statements are not available with this option. A comprehensive list of incompatible features can be found here.
Statement
This is the most granular option. Connections are returned to the pool after every statement. Transactions with multiple statements are not allowed. This is best used when AUTOCOMMIT is in use.
Finding the connection pool config
- Go to the
Settingssection. - Click
Database. - Find your Connection Info and Connection String. Connection pooling is on port
6543.
Connecting with SSL
Use this when connecting to your database to prevent snooping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Obtain your connection info and Server root certificate from your application’s dashboard.
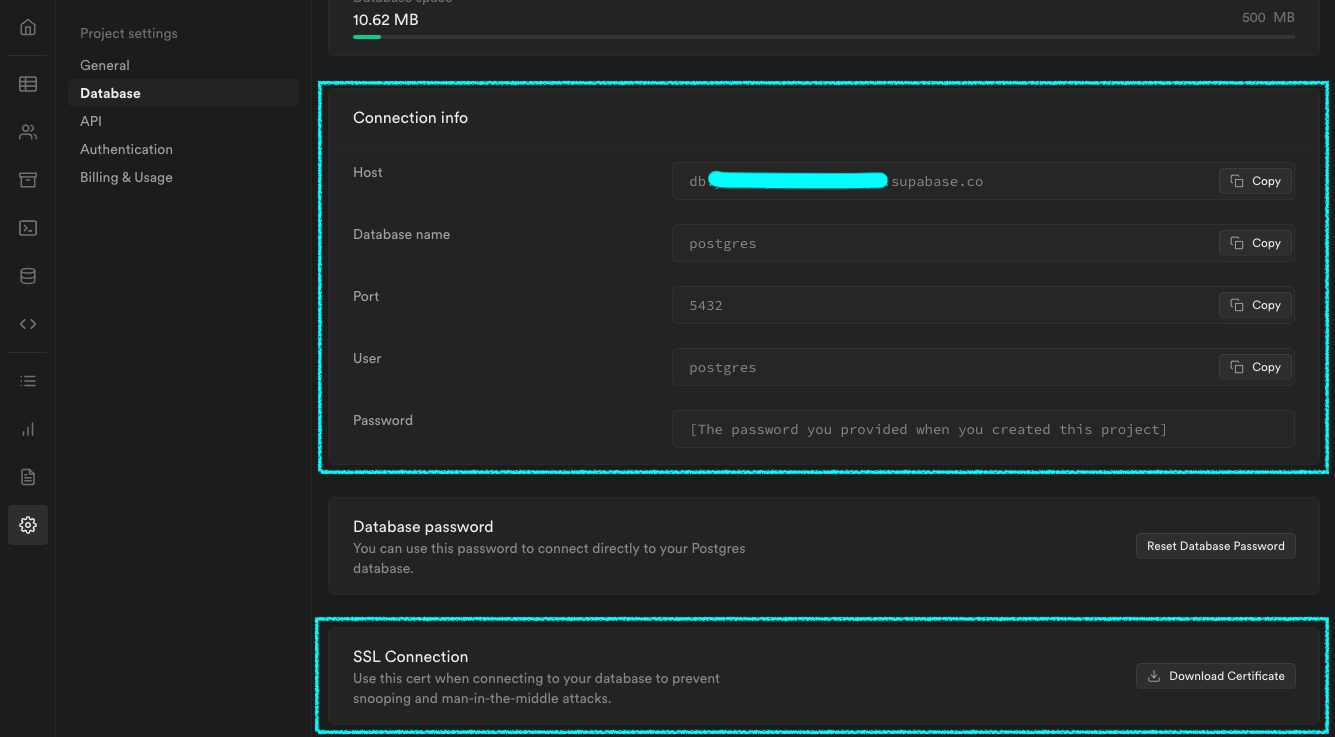
Assuming you’ve downloaded your certificate and it’s located at $HOME/Downloads/prod-ca-2021.cer, and your Host address is db.abcdefghijklm.supabase.co you can connect to the DB with
SSL enabled as illustrated below:
- With
psql
psql "sslmode=verify-full sslrootcert=$HOME/Downloads/prod-ca-2021.cer host=db.abcdefghijklm.supabase.co dbname=postgres user=postgres"
With
pgAdmin
a. Register a new Postgres server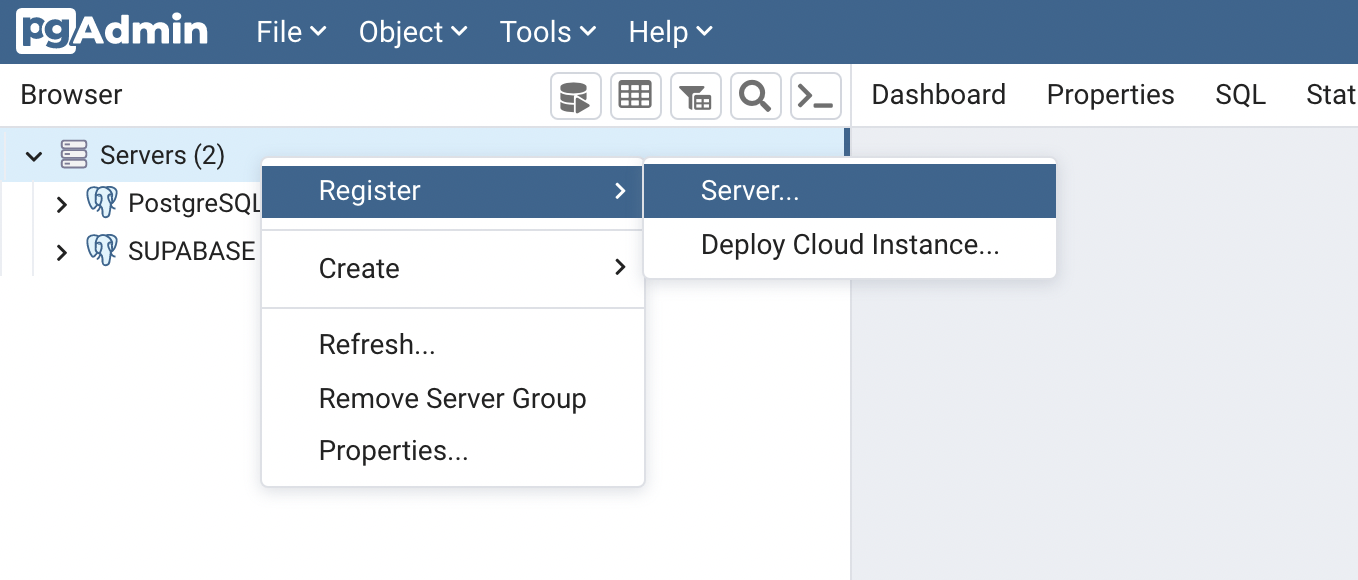
b. Name your server to your liking and add the connection info.
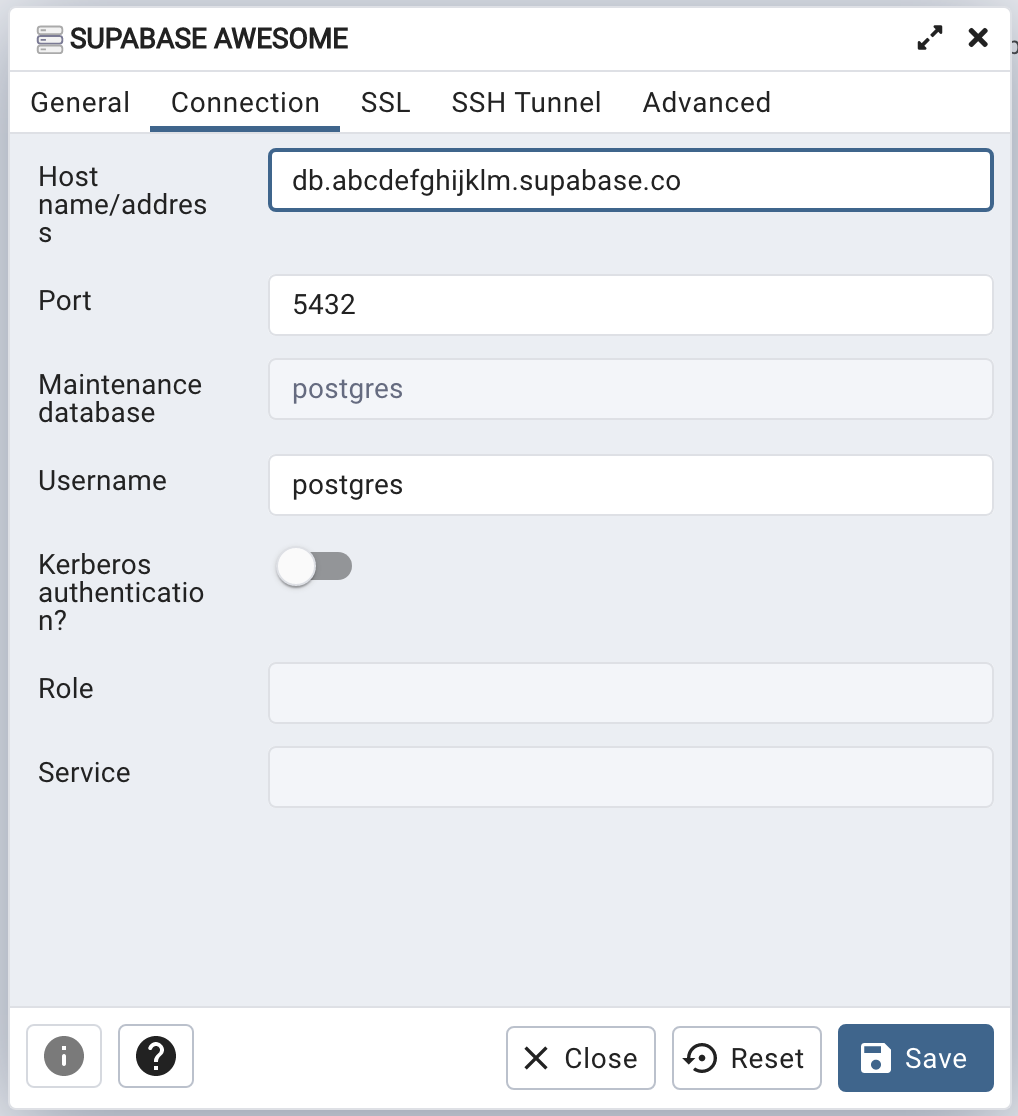
Navigate to the SSL tab and change the SSL mode to Require. Next navigate to the Root certificate input, it will open up a file-picker modal. Select the certificate you downloaded from your Supabase dashboard and save the server details. PgAdmin should now be able to connect to your Postgres via SSL.